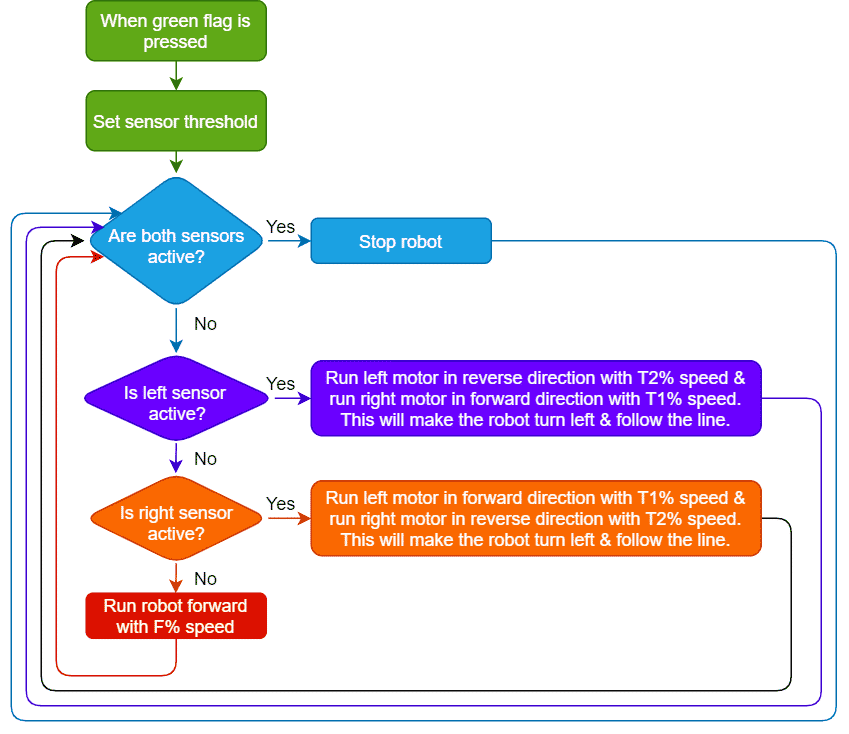
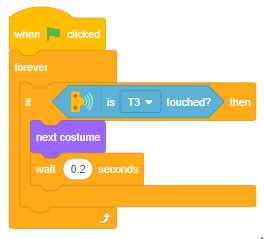
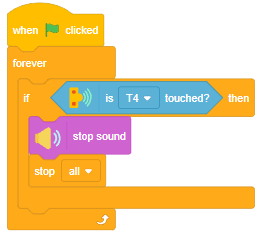
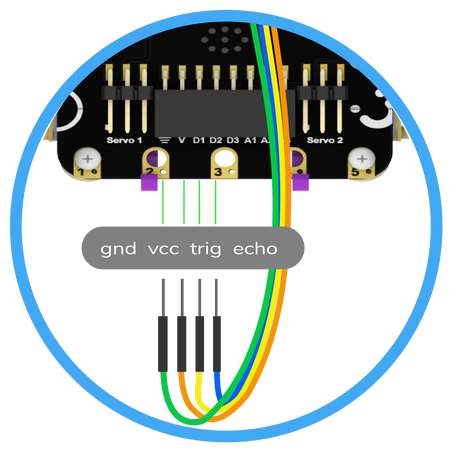
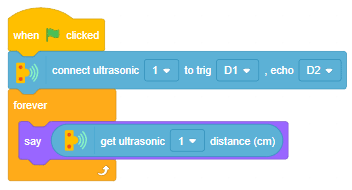
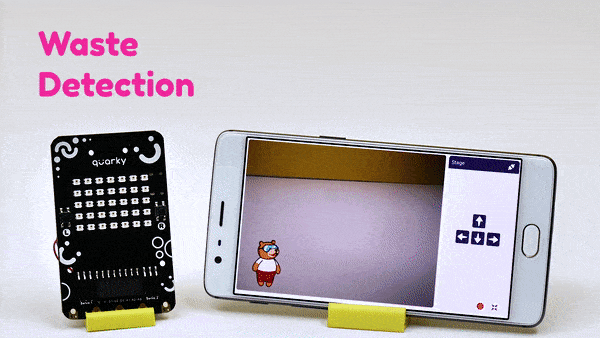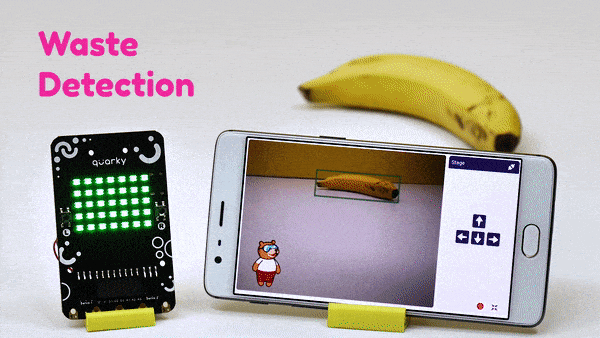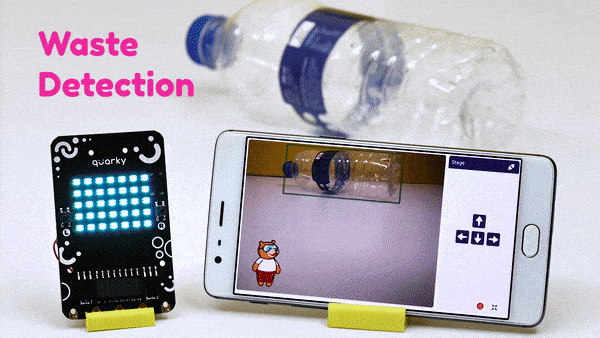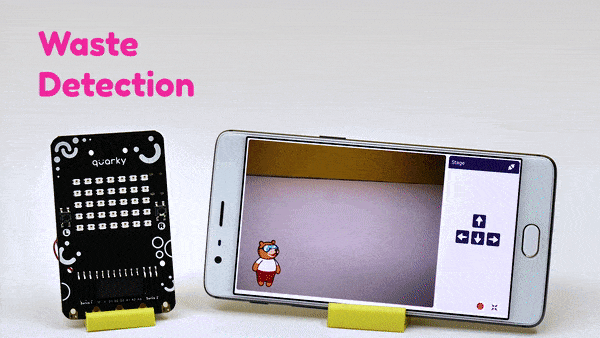
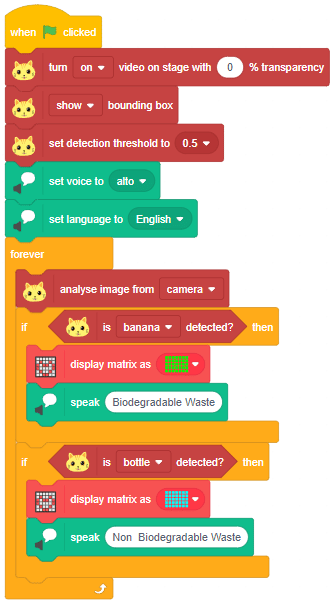
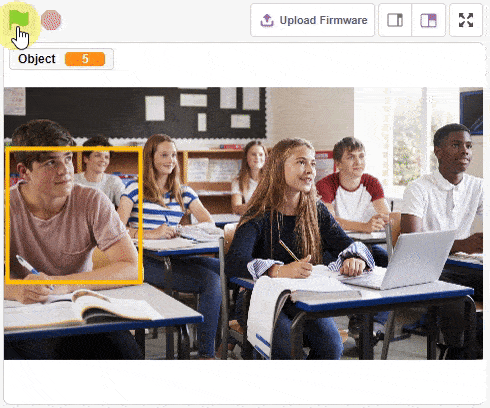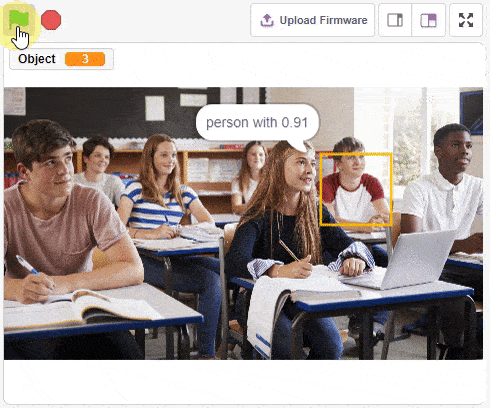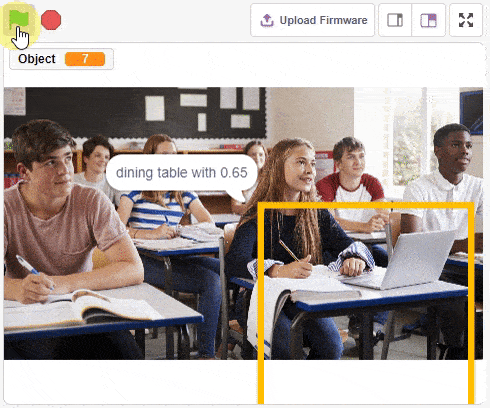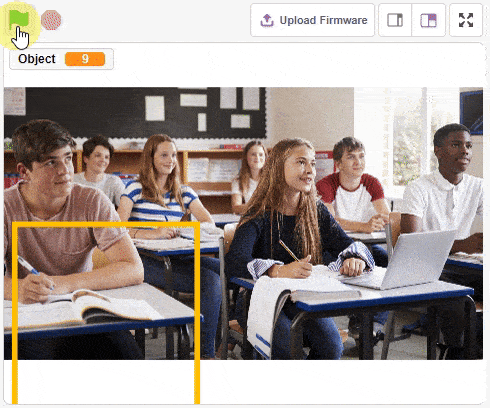
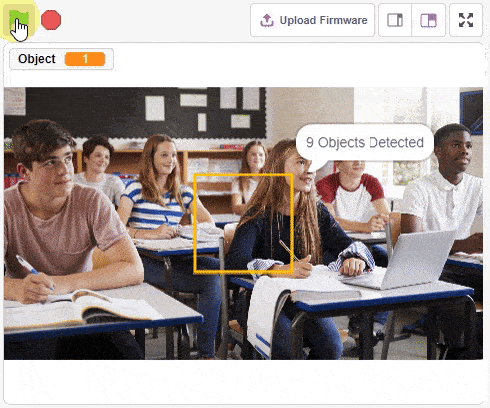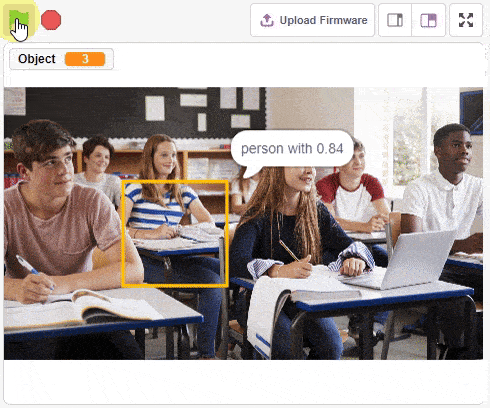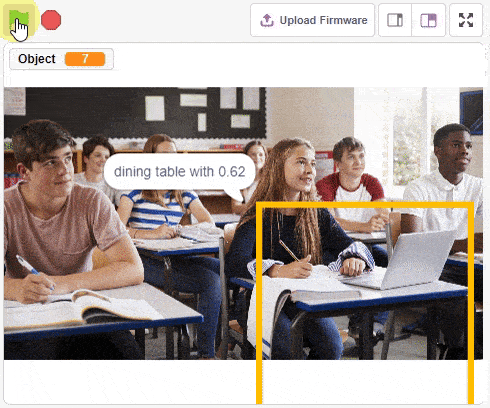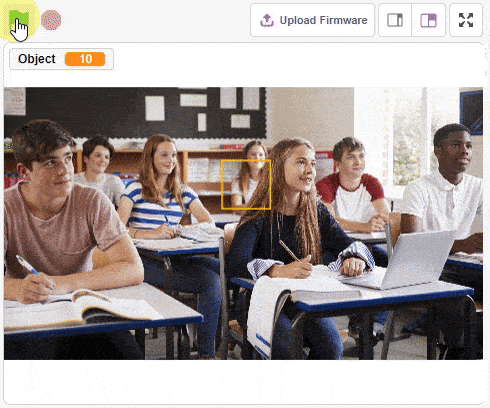
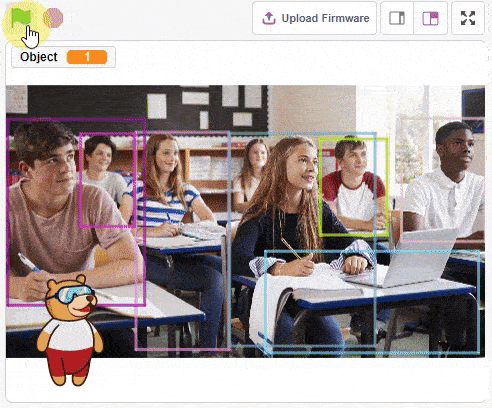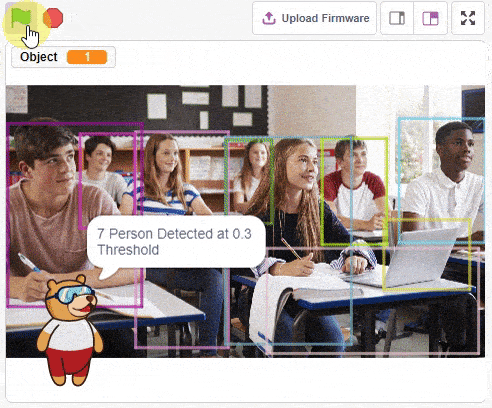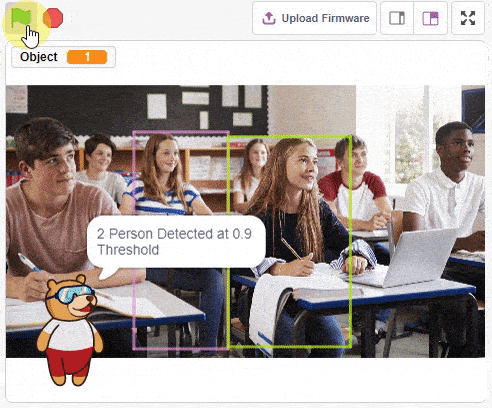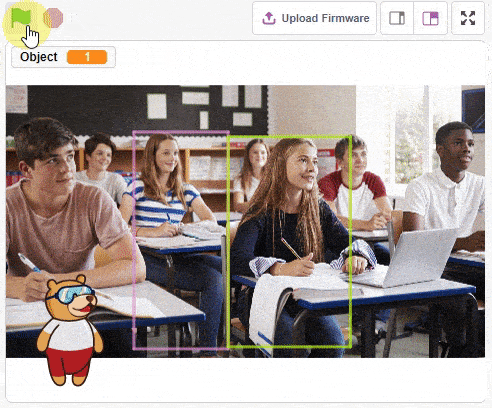
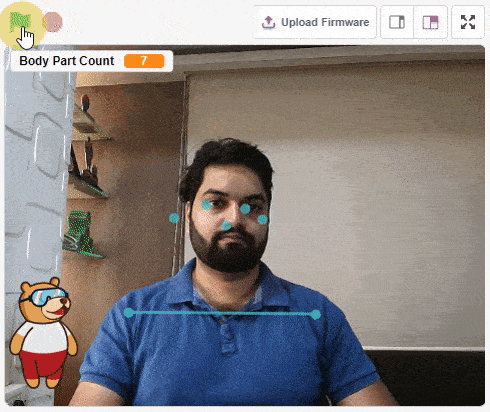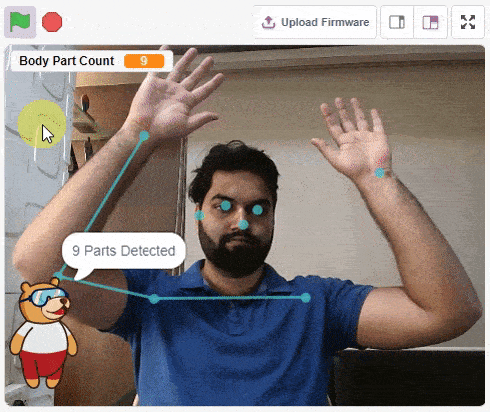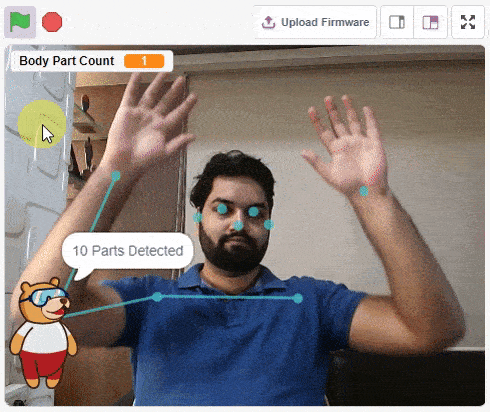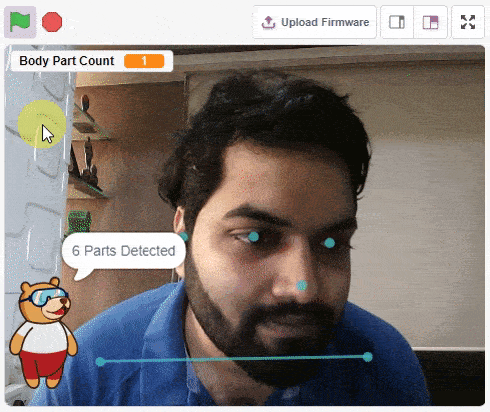
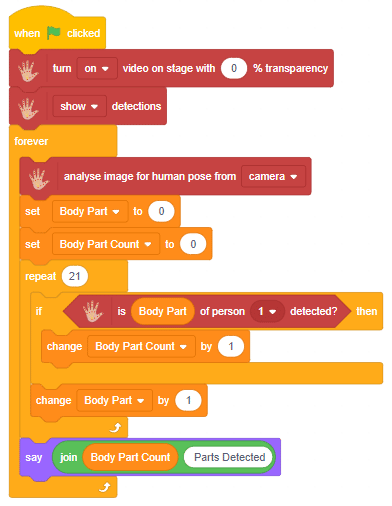
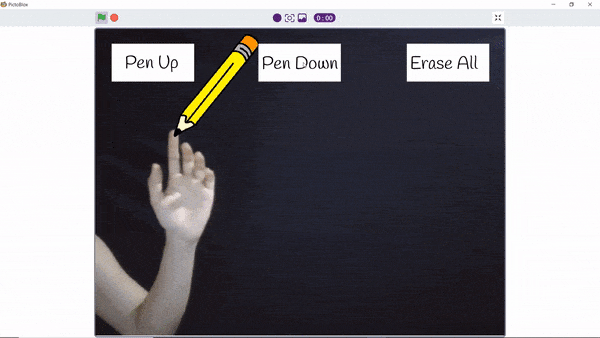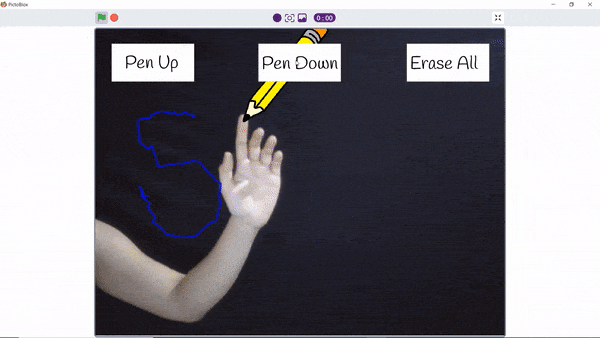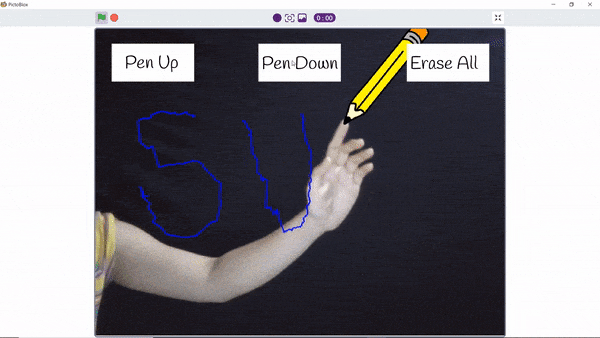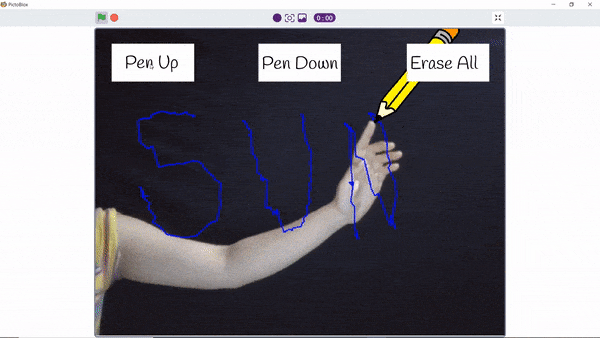
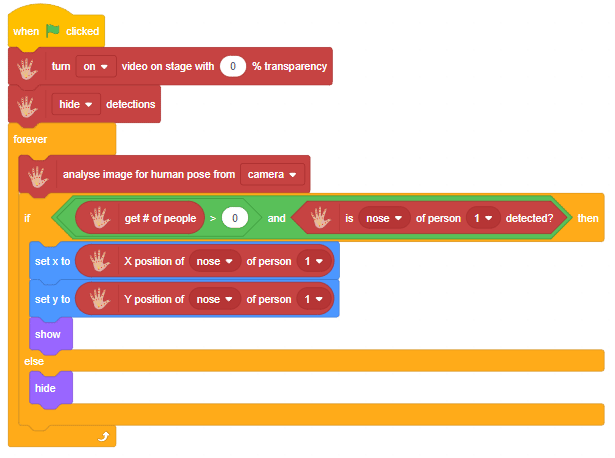
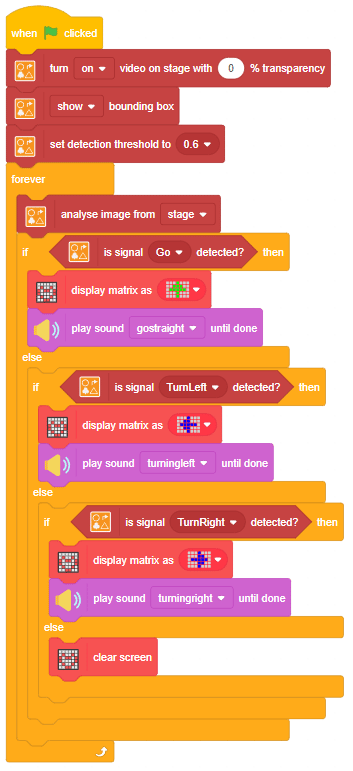
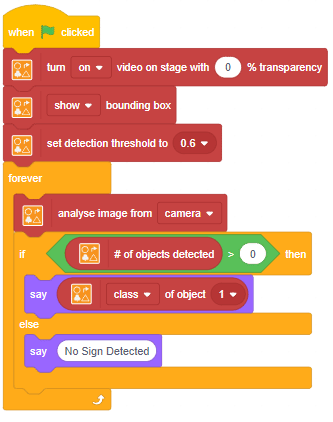
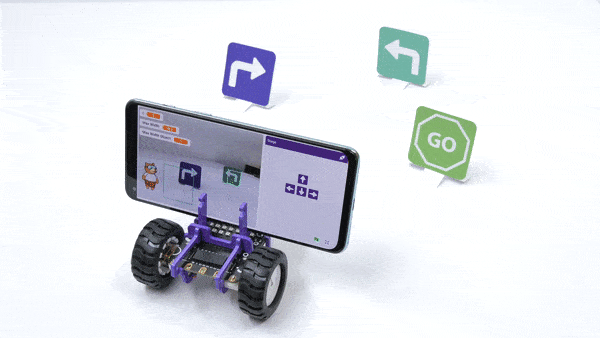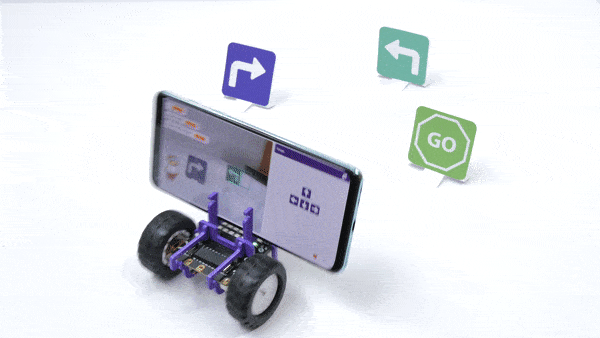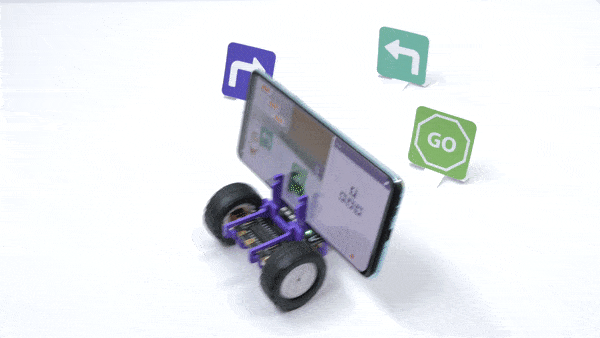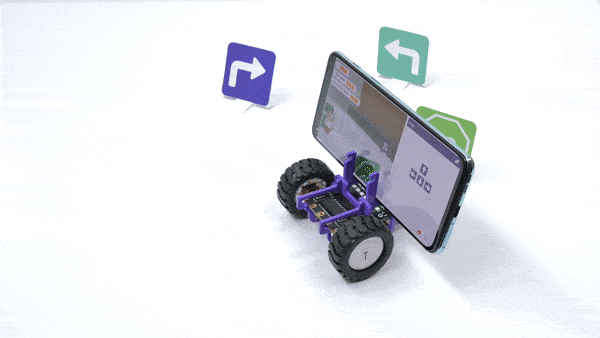
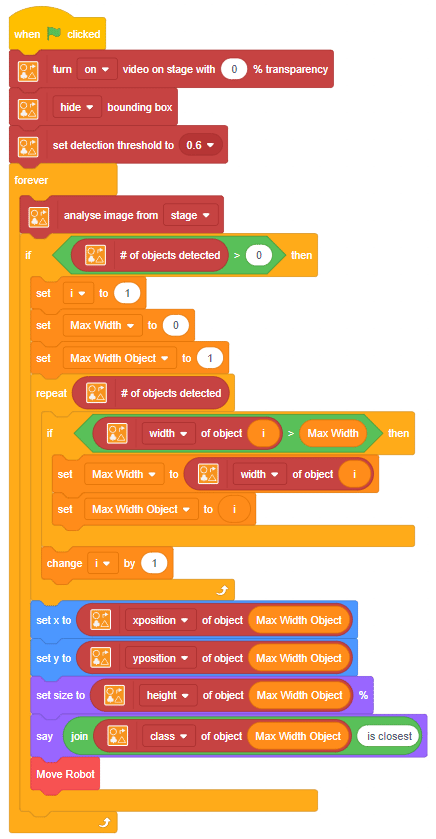
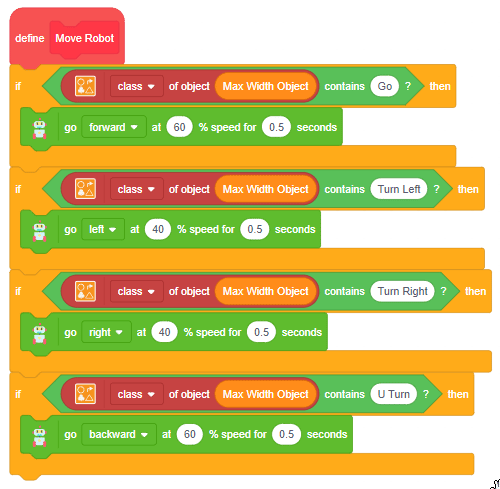
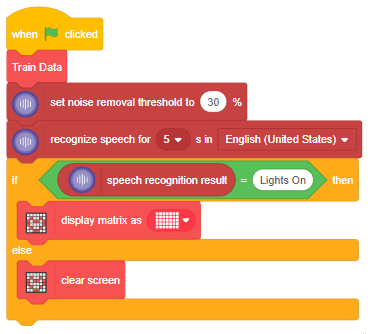
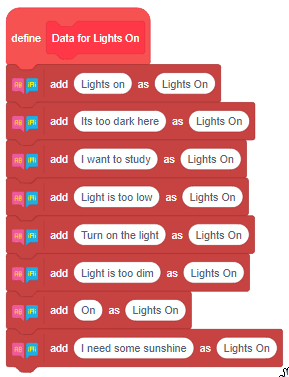
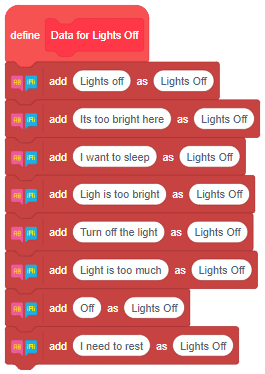
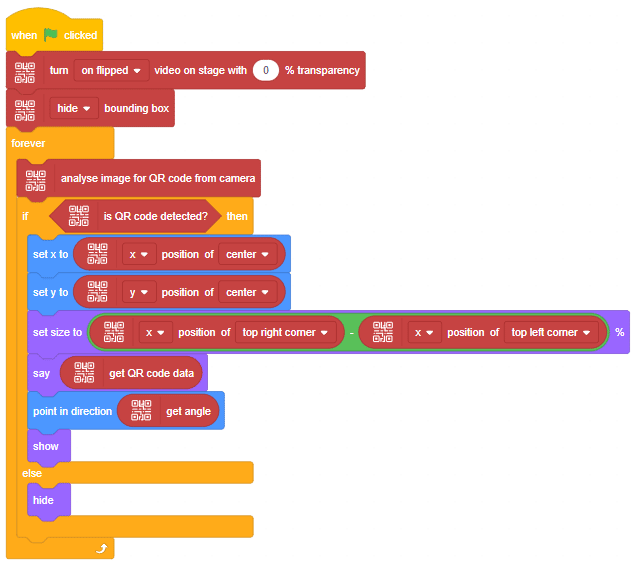
The function initializes the following line parameters for the Quarky robot – F. T1 and T2:
There are 3 important things we will use in a line following robot:
- F: The speed with which the robot will move forward when it has not detected a black line.
- T1 & T2: When the robot is following the line and if one of the sensors says the left one, detects the black line, then the robot is off track and has to turn left in order to get back on track. And we know how to turn the robot left. The left motor moves backward and the right move forward. But if both are moving at the same speed, then the robot’s motion will become jerky and inefficient. Hence we will have two speeds for turning T1 and T2, where
- T1 will be the speed with which the motor will move forward and
- T2 will be the speed with which the motor will move backward.
The user will have to set F, T1, and T2 during the programming and calibrate it for effective line following.